5 Benefits of Polio:
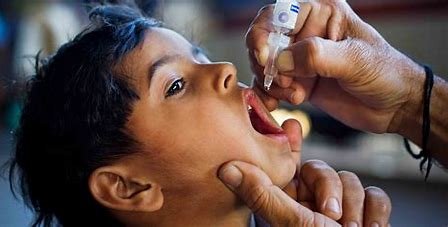
- Prevention of Polio Infections: One of the most immediate and evident benefits of the polio vaccine is its ability to prevent polio infections. Polio, caused by the poliovirus, can lead to paralysis and, in severe cases, death. The vaccine works by priming the immune system to recognize and combat the poliovirus, thereby significantly reducing the risk of infection. This prevention not only spares individuals from the pain and suffering associated with polio but also curtails its spread within communities.
- Eradication Efforts: The widespread administration of the polio vaccine has been pivotal in global efforts to eradicate the disease. Through initiatives like the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI), which leverages vaccination campaigns, surveillance, and community engagement, significant progress has been made towards eliminating polio altogether. Vaccination plays a central role in these efforts by creating immunity barriers within populations, ultimately leading to the interruption of poliovirus transmission chains.
- Protection of Future Generations: By vaccinating against polio, we not only protect current generations but also safeguard the health and well-being of future generations. Through herd immunity, wherein a sufficiently high proportion of the population is immunized, the spread of the poliovirus is impeded, even among those who are not vaccinated. This collective protection ensures that vulnerable individuals, such as newborns and those with compromised immune systems, are shielded from potential polio infections.
- Economic Benefits: The economic impact of the polio vaccine cannot be overstated. By preventing cases of polio-related disability and death, the vaccine averts significant healthcare costs associated with treatment, rehabilitation, and long-term care. Moreover, the eradication of polio will lead to substantial economic gains due to increased productivity, as individuals are spared from the lifelong disabilities that can result from the disease.
- Preservation of Achievements: The success of the polio vaccine serves as a testament to the power of vaccination programs and public health initiatives. It underscores the importance of sustained investment in immunization infrastructure, research, and advocacy to combat not only polio but also other vaccine-preventable diseases. By preserving and expanding upon the achievements made in polio eradication, we pave the way for future victories in public health.